By Swaraj Raghuwanshi and Aastha Suri
India has witnessed a significant increase in train accidents by 37% in the year 2022-2023, thereby posing a threat to the safety and lives of passengers. Such accidents not only result in loss of lives but also cause severe injuries and damage to property[1]. The recent Balasore train accident, which claimed the lives of 288 individuals and injured over 1000 people, serves as a critical warning sign for the Indian Railways[2]. The Balasore train accident in Odisha occurred when the Coromandel Shalimar Express and the Yeshvantpur Howrah Superfast were nearing their speed limits of 130 kmph. Although, the speed was not the primary cause of the accident, the entire scenario emphasizes the importance of ensuring that the safety measures are in place when increasing train speeds. The investigations further revealed that signal failure resulted in the Coromandel Shalimar Express moving towards the loop line instead of the main line, leading to a collision with a stationary freight train. The impact was significant, derailing the Coromandel Shalimar Express and causing some of its coaches to collide with the three two coaches of the Yeshvantpur-Howrah Superfast train[3],[4],[5].
Such devastating train accidents highlight the urgent need for adopting innovative patent technologies to enhance train safety and prevent the occurrence of such accidents in the future.
Determining the cause of the accident:
While the CBI investigation is in process, the initial statements by the railway officers suggest that the signal failure occurred due to human intervention or negligence. The relay room, where signaling and telecommunication equipment is housed, played a crucial role in the accident, however, the investigators are focusing on identifying individuals responsible for any tampering or maintenance error that led to the incorrect setting of the point machine, causing the signal failure. This incident raises various concerns about the vulnerability of the rail safety mechanism in India and the need for comprehensive improvements.[6]
Though, several patented technologies and innovations in train safety exists, which can prove to be helpful for Indian Railways for addressing the increase in number of the train accidents, and preventing such accidents. Several technologies and systems have been proven successful in preventing accidents and reducing human error to a certain extend in rail networks worldwide. Some examples of such patented technologies are disclosed herein below:
| Application Number | Title | Technology Details |
| EP2210791A1 | Automatic train protection and stop system | an Automatic Train Protection (ATP) technology employing sensors and communication technology to automatically control train speed, ensuring compliance with speed limits and signal indications |
| EP2371661A2 | Train Information Exchange | |
| US9434397B2 | Positive train control system and apparatus therefor | Positive Train Control (PTC) technology that employs GPS and wireless communication for allowing for real time monitoring and control of train movements, preventing collisions and over speeding. |
| CN101179710B | Intelligent video monitoring apparatus of railway crossing | The technology relates adoption of intelligent video surveillance for providing an additional layer of security and safety. These AI systems are able to detect suspicious activities, identify potential hazards, and alert authorities in real-time. |
| CN202189444U | Railway station intelligent security monitoring commanding system |
Another one of the innovative technology that can avert rail accidents is KAVACH, which has been successfully implemented over the South Central Railway Zone (SCR. During its development stage, KAVACH was initially deployed across sections like Wadi – Vikarabad – Sanatnagar and Vikarabad – Bidar sections over South Central Railway, covering over 264 Kms and 25 stations. During 2020-21, Kavach was further implemented for another 322 Kms, covering 32 stations. In financial year 2021-22, it was further implemented for another 859 Kms, covering 77 stations and thus the total deployment of Kavach increased upto 1,445 Kms (including 68 RKms of Automatic signaling), covering 133 stations, 29 LC Gates and 74 Locomotives. The sections covered under the system include – Manmad – Mudkhed – Nizamabad – Sitafalmandi – Kurnool – Guntakal (excluding Secunderabad and Guntakal Stations); Parbhani – Bidar – Vikarabad – Wadi and Wadi – Sanatnagar[7], [8].
With a a focus on enhancing safety and preventing accidents, Indian Railways is actively expanding expanding the implementation of Kavach by deploying it on on Delhi-Mumbai and Delhi-Howrah corridors. Recognizing these high-density routes as prone to accidents, the railway authorities have prioritized deploying the KAVACH system. As train often operate in close proximity on these busy corridors, the integration of KAVACH aims to optimize safety measures and minimize potential risks [9],[10].
Understanding KAVACH and its Implementation:
Kavach is an automatic train protection system designed to prevent accidents caused by human errors, including crossing red signal indicating danger, and thus avoiding collision; and prevent damages occurring due to over speeding by engaging with the braking system of the train. Further, the Kavach system prevents the collision between two locomotives. The system operates by bringing locomotives to a halt when they approach towards each other within a distance of 380 meters. Furthermore, in case of emergencies, the Kavach system also relays SoS communications[11].
The Indian Railways has allocated ₹ 272.30 crore in the financial year 2022-2023 for the installation of Kavach along 34,000 kilometers of tracks[12]. The implementation plan prioritizes high-density network routes, which account for 96% of railway traffic. This strategic approach aims to enhance passenger safety in heavily trafficked areas. Although Kavach is a promising approach in preventing accidents, its impact depends on its coverage and proper functioning in critical situations.
One of the least expensive SIL-4 certified technologies, Kavach, has 1 in 10,000 year error probability[13]. Currently, Kavach is deployed on 1465 route kilometers in South Central Railway, safeguarding 77 trains[14]. However, its effectiveness in averting a specific accident is limited if the section is not covered by Kavach, or in case of incorrect settings in the relay room. In case of any mismatches, that is, when the point is not setting properly or a relay is not picking up and thus signals is not operating, in such rare scenarios, Kavach may not be of much use. In this situation, the station master notifies the electrical signal maintainer and provides the maintainer with the key to the relay room so that they can make the necessary relay and circuit adjustments. However, it is not always possible to temporarily halt the traffic for maintenance due to the large number of trains that are waiting to move forward. This may be dangerous and may further leads to scenarios like the Balasore case, when the route and the signals were out of sync[15].
Therefore, a comprehensive approach encompassing robust infrastructure, training and maintenance protocols is necessary for a fail-safe mechanism.
Trends in Innovations related to Railway Safety in India:
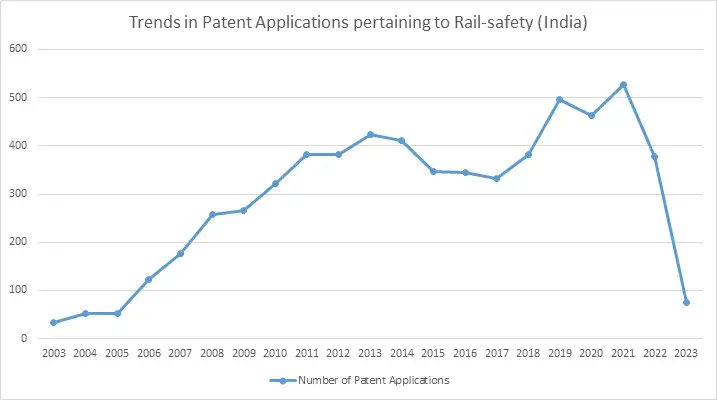
Over the years, there has been a noticeable increase in the trend of filing patents related to railway safety in India. With a growing emphasis on improving safety measures and reducing accidents, inventors and organizations have shown a greater interest in developing innovative solutions for the railway sector. The graph provided depicts a trend in the number of patent applications filed in India, pertaining to rail-safety related innovations.
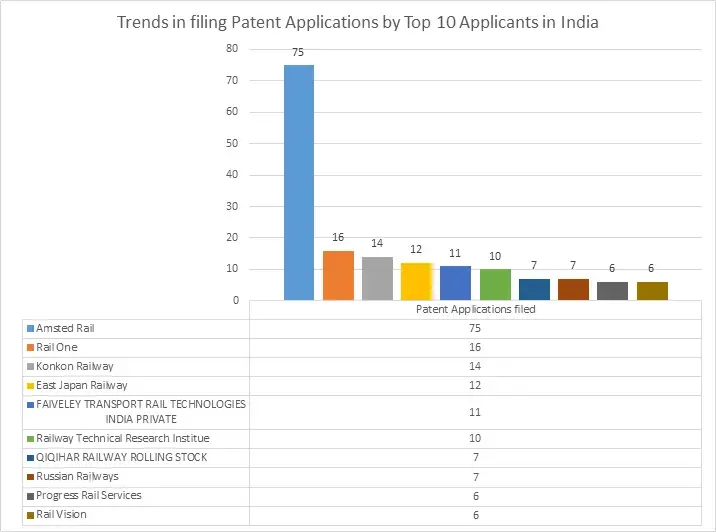
The graph provided below illustrates the trend in the number of patent applications filed in India for rail safety related inventions by top applicants in India, is provided below herein.
The Indian Railway has potential to drive a significant increase in the filing of patents by actively adopting patented technologies. The Indian Railway can create favorable environment that encourages and motivates individuals to file their own patent applications.
Additionally, the government has introduced initiatives to foster innovation and entrepreneurship in India to engage with startups, entrepreneurs, and innovators to develop innovative solutions for the railway network. Although the government has introduced such initiatives, the pace at which these innovations are being adopted in the vast railway network remains relatively low. However, the subsequent paragraph elaborates on the Indian Railways’ policy to promote innovation and collaboration in more detail. It is crucial for the government and railway authorities to expedite the evaluation and implementation process, considering the scale and complexity of the railway system. By streamlining the adoption of these innovative solutions, the railways can effectively harness the potential of these novel technologies to enhance safety and ensure the well-being of the passengers and staff alike.
Indian Railways’ Policy to Promote Innovation and Collaboration:
The Government of India has introduced several initiatives to foster innovation and entrepreneurship in India. As part of such efforts, the Indian Railways has formulated a policy to engage with startups, entrepreneurs, and innovators to develop innovative solutions for the railway network. This policy aims to provide seed fund support to startups, encourage the development of functional prototypes, and promote the adoption of emerging technologies to enhance the operational efficiency and safety of the Indian Railways. The policy has three main objectives provided below:
- To develop cost-effective and scalable solutions for improving quality, reliability, and maintainability in the Indian Railways;
- To leverage innovative technologies for enhancing operational efficiency and safety; and
- To foster an innovation culture in the railway sector through co-creation and co-innovation.
The policy further extends its support to startups recognized by Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Indian Companies primarily classified as Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), individual innovators, and research and development institutions. Partnerships, companies and limited liability partnerships incorporated under relevant laws are also encouraged to apply.
The Indian Railways’ policy to engage with startups and innovators showcase the government’s commitment of fostering innovation and entrepreneurship in the country. By providing seed fund support and collaborating with innovators, the Indian Railways aims to develop cost-effective and reliable solutions to address the technological needs of the railway network and safety.[16]
Conclusion:
Considering all the factors, the recent increase in train accidents in India highlights the urgent need for the Indian Railways to prioritize train safety and adopt innovative patent technologies. Further, by considering diverse perspectives and embracing a range of inventions and innovations, the Indian Railways can significantly enhance the safety, efficiency and reliability of the train operations. The implementation of an advanced signaling systems, intelligent braking technologies, track monitoring solutions and video surveillance systems can be life changing and may ensure a safer journey for millions of passengers.
[7] https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/explained-understanding-the-kavach-system/article66930707.ece
[8] https://scr.indianrailways.gov.in/view_detail.jsp?lang=0&dcd=17664&id=0,5,268
[9https://www.metrorailnews.in/kavach-indias-train-safety-system-developed-by-indian-railways/
[10] https://www.studyiq.com/articles/kavach-train-protection-system/ – https://www.studyiq.com/articles/kavach-train-protection-system/
[13] least expensive SIL-4 certified technologies, Kavach, has 1 in 10,000 year error probability
[14] https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/explained-understanding-the-kavach-system/article66930707.ece