PATENTS IN ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY IN INDIA
Electronics Industry in India
India share in global hardware electronics production has been increased from 1.3% in 2012 to 3% in 2018[1]. There is significant growth in digital technologies and adaption of high-end technology such as Internet of Things (IoT), 4G/LTE networks and roll out of 5G.
Semiconductor industry sector is the most important sector in the electronics industry. Semiconductors and associated passive components are the basic elements in electronic technology. Such technology is required by large number of industries: including telecommunications, information technology, industrial machinery and automation, medical electronics, automobile, engineering, power and solar photovoltaic, defence and aerospace, consumer electronics, and appliances.
Criteria for Patent in India
For an Electronic Invention to be patentable[2], the criteria are as follows:
- It should be novel: invention should not have been published or used anywhere in the world before the date of filing the patent application in the patent office.
- Must involve an inventive step: a feature of invention should involve a technical advancement as compared to existing knowledge or having economic significance or both
- Capable of industrial application: invention is capable of being made or used in an industry
- It should not fall under the categories of inventions that are excluded from patentability under the concerned jurisdiction
Of all the electronic invention, patent for software or computer program is questionable all over the world, so does in India. Software which is an important part of the electronic devices and electronic controlled devices, are excluded from the scope of patentable invention in India under Section 3(k) of the Indian Patent Act i.e. a mathematical or business method or a computer programme per se or algorithms, are not patentable.
Computer programs with technical application in industry and embedded in hardware are considerable for patent protection.
Software related inventions patented in are-
- Siemens was granted patent No. 195440 in respect of a method for testing system components of an object-oriented program.
- Philips Electronics was granted patent No. 194663 in respect of an interactive entertainment apparatus operable to output sequences of image frames.
Electronics Industry and Patents
Following foreign and Indian companies are amongst the top companies that file patent applications for electronic inventions in India:
- Qualcomm Incorporated
- Samsung India Software Operations Private Limited
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
- Philips Electronics
- LG Electronics Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericssion (Publ)
- Thomson Licensing
- Huawei Technologies Co.Ltd.
- Sony Corporation
- Dell Products
- Koninklijke Philips Electronics
Source: Orbit
Patent Filing Trend & Electronics Industry
As per IPO annual report, the number of applications for patents filed in 2017-2018 was 47, 854 reflects an increase of 5.3%[3] in overall filing which were 45,444 in 2016-2017. The filing trend shows modest growth in almost every field of technology, except in the field of computer/electronics, general engineering, polymer science and technology and metallurgy & material science Detail of filing trend of application of different field of technology is below.
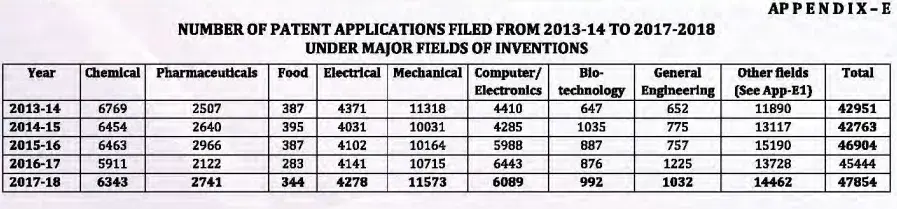
Source: Annual Report 2017-18 published by the Indian Patent Office
Further, the number of patents granted in the field of computer/electronics with the Indian Patent Office in the year 2017-18 were 1028. The patents granted from the year 2013 to 2018 is shown below:
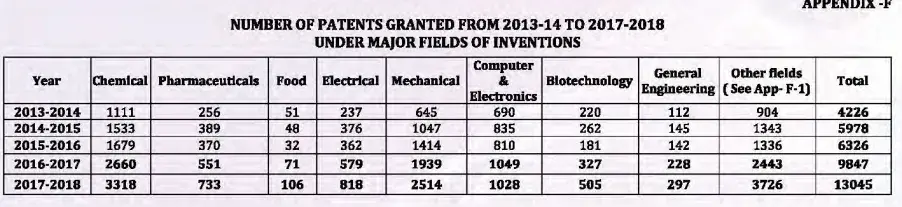
Source: Annual Report 2017-18 published by the Indian Patent Office
Government Policy to boost Patents in Electronics Industry in India
“An India where Intellectual Property stimulates creativity and innovation for the benefit of all” is the vision of our National IPR Policy.
The market for electronics products in India has shown significant increase and the demand for electronics hardware in the country is projected to increase by US $228 Billion by 2020 from over US $ 100 Billion in 2016-17[4]. Creating opportunities for companies in the ESDM sector to meet the increasing demand and also India to become next export hub. Initiatives like Make in India, Digital India, Skill India, and Start up India and Atal Innovation mission proven to be catalyst to electronic manufacturing.
Recent initiatives[5] taken by Indian Government in this regard are-
- Target to achieve turnover of USD 400 billion by 2020 involving investment of over USD 100 billion and employment to around 28 million people. This includes USD 55 billion in chip design and embedded software industry;
- Setting up over 200 Electronics Manufacturing Clusters (EMCs);
- Upscale education to over 2500 PhDs annually by 2020;
- Transform India into global hub for Electronics System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM);
- Current proposals of USD 10.503 billion investment include:
| Investment size (approx) | Technical field |
| Rs 52,000 crore (USD 8.4 billion) | Semiconductor wafer fabrication |
| Rs 791 crore (USD 127 million) | Consumer electronics and appliances |
| Rs 8218 crore (USD 1.3 billion) | Hand held devices and telecom |
| Rs 1990 crore (USD 321 million) | LED fab and LED products |
| Rs 710 crore (USD 114 million) | Automotive electronics |
| Rs 62 crore (USD 10 million) | Solar photovoltaics |
| Rs 210 crore (USD 34 million) | Strategic electronics |
| Rs 750 crore (USD 121 million) | Semiconductor ATMP |
Source: National Policy on Electronics[6]
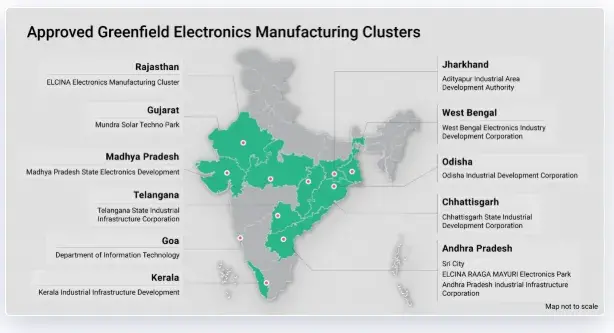
Source: Electronics Manufacturing Clusters (EMCs)[7]
Patent Agents, Engineers, Analysts and Lawyers assist client’s right from Patent Searching to Patent prosecution of patents pertaining to mechanical engineering. These teams meticulously works on drafting of such patent applications as well as replying to Office Actions.
[1] https://www.investindia.gov.in/sector/electronic-systems
[2] https://meity.gov.in/content/patents
[4] https://www.investindia.gov.in/sector/electronic-systems
[7] https://www.investindia.gov.in/sector/electronic-systems
For more information on Patent Rights & electronic industry in India please contact us at info@ssrana.com or submit a query.
Read More
PATENTS IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING INDUSTRY IN INDIA
Scope of Mechanical Engineering & Industry in India:
The ambit of mechanical Engineering & industry brings under it’s microscope every manufacturing activity that takes place as mechanical engineers design power-producing machines, an example of it could be motor engines, different kinds of generators, steam and gas turbines, internal combustion engines are some examples that have been given for your kind reference. As Conveyor systems and automated transfer stations are examples of material handling systems, which are designed utilizing the skills and expertise of a Mechanical engineer. The use of their skills extends to machineries and sectors that are a part of our day-to-day lives such as elevators, refrigerators and mixer machines which are utilized at every construction site there is.
Mechanical is a domain, which has a wide arena, under which sectors such as designs, production, aerospace and mechatronics take cover as mechanical and machinery design can build sensitivity control system with the assistance of the electronics sector similar to integration of sensors, controllers, and machinery.
Computer Aided Design (CAD) is software, which assist mechanical engineers in development and analysis of designs in process and further, runs stimulations to test how a machine is going to function, interact with the connected systems and provide specifications required for the parts. As there main work is to find faults in the manufacturing and hence, rectify the said errors.
It should be noted that from April 2000 to December, 2019 the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into India’s mechanical and engineering industries stood at US$ 3.63 billion, as per the information published by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).[1]
Developments that have taken place in the MechanicalEngineering & Industry:
The part played by a mechanical engineer is to deliver the idea in his mind to the doorsteps of innovation and make it accessible for everyone to use and they undertake manufacturing activities of anything that moves from complex machinery to every minute device. Mechanical engineers need to ensure that his basics of material, fluid and solid mechanics, thermodynamics, heat transfer, design, instrumentation are clear and his knowledge is in consonance with the latest trends and developments as well. With time the field of mechanical studies has evolved and given birth to specialized mechanical fields such as biomechanics, nano-mechanics, mechanisms, micro power generation, tribology (friction and wear), and vibrations cartilage-tissue engineering, energy conversion, laser-assisted materials processing, combustion, MEMS, microfluidic devices, fracture mechanics. Ideas lead to development; innovations and modification of devices or processes undertaken so as to provide solutions to the modern day problem and lead us into the future. It is proficiency that ensures to more effective products, processes, innovation, technological services to the market so that they are readily available to the public.[2]
Patents & Mechanical Engineering & Industry:
Literature available on Patent is an eminent source for technical research and the information is available for all to access whether they are researchers, government organizations, patent attorney, inventors, privates companies or licensors among other stakeholders that can take advantage of the information at hand by referring to the databases available to get a better understanding of what is out there in a specific sector of science and technology. Globally there are about 80 million patent documents available[3].
Patents are the most relevant and apt source of technical information available but often they are not referred to appropriately as if referred under appropriate circumstances and utilized efficiently it would lead to effective R & D, effective planning and productive strategies. A thorough prior search is essential before initiating a process for development and innovation of a new mechanical process as they are useful as follows:
- That patents are primary and verified sources of information.
- That it apprises the user of it’s use and working
- That often the description can help you capture a particular market more effectively.
- That targeting a particular inventor with a specific research area can be used as an aid to the growth of the company and the sector.
Patent Filing and Mechanical Engineering & Industry
Before discussing India’s patent scenario, we will consider the world patent scenario[4] till 2018. As shown in Fig 1. The scenario depicted in the figure shows that there were approximate 30 lakh patents filed in different patent offices worldwide and it shows 5.2 % increase over previous year. Table 1 shows the total number of applications for patents received from Indian residents and non-residents through various routes, during the period from 2008-2009 to 2017-18.[5] It is observed that there is tremendous increase in number of patent applications filed by foreign companies in India. As India is a developing country, it has to really look into the patent filing trend from outside countries and also must find the incentive behind it.
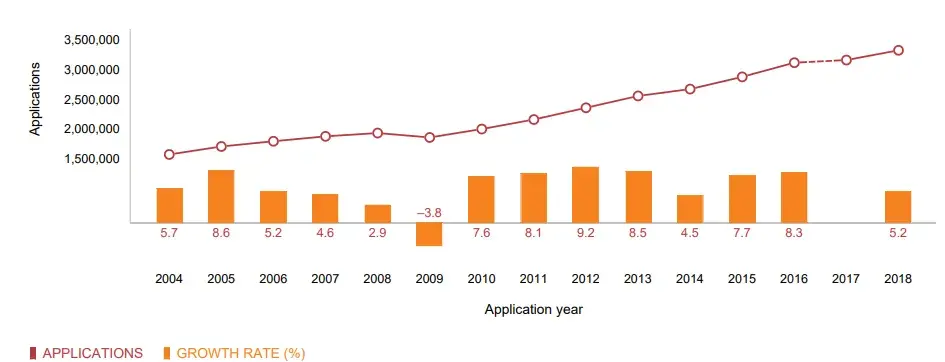
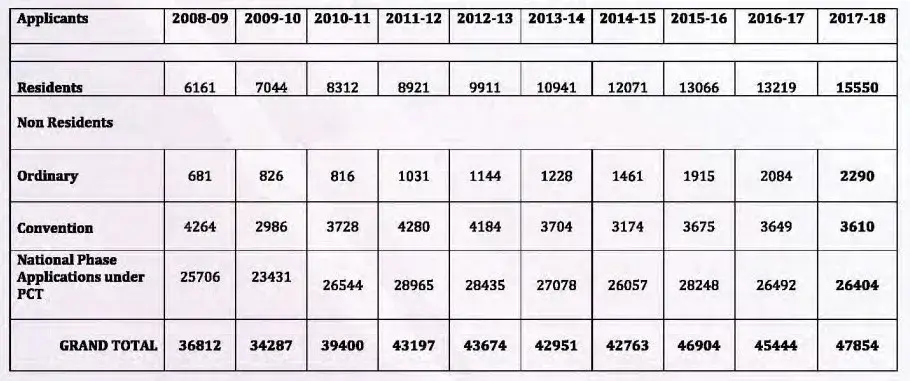
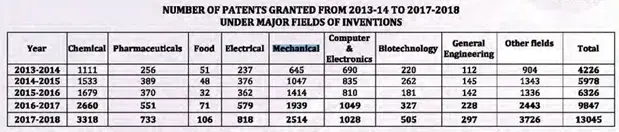
As per the Annual Report 2017-18[6] published by the Indian Patent Office, the total number of patents granted during the year was 13,045 out of which 1,937 were granted to Indian applicants. The number of patents in force was 56,764 as on 31st March 2018, out of which 8,830 patents belonged to Indians. Out of the total granted patents, 3,318 patents were granted to applications relating to the Chemical, 2,514 to Mechanical, 1,028 to Computer Science and Electronics, 1031 to Communication, 773 to Pharmaceuticals, 818 to Electrical, 505 to Biotechnology etc.
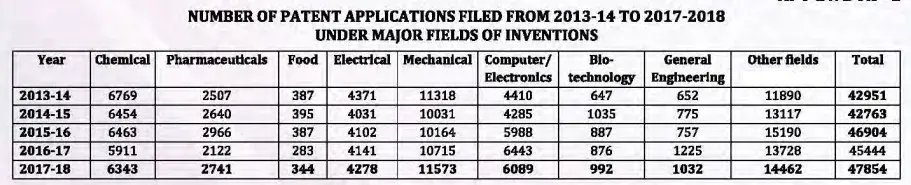
Table 2, shows there is an increase in number of filing patent applications under mechanical field of invention from year 2013-14 to 2017-18, however, it is more particularly observed during 2013 to 2018 when compared with any other fields of invention. Table 3 shows the data for inventions which are granted related to “mechanical engineering” and other fields of invention. It can be seen that there is a constant increase in this field of invention from the year 2013.
Patent Facilitation Cell (PFC):
The Department of Science & Technology (DST) established a Patent Facilitation Cell (PFC) [7] at TIFAC in 1995 and subsequently 24 Patent Information Centers (PICs) in various states under Patent Facilitation Programme (PFP) of DST, to create awareness and expand support for intellectual property rights (IPR) including patents, copyrights, geographical indications, etc. at the state level. These PICs have also established Intellectual Property Cells in universities (IPCUs) of their respective states to expand the network. Till date, 84 IPCUs have been created at various state universities. In addition, they are also responsible for providing assistance to inventors from Government organizations, State University, for patent searches to find out the potential and evaluation of inventions.
Mandate of the Patent Facilitation Cell are as follows:
- Providing Patent information as a vital input to R&D
- Patent /IPR facilitation to academic Institutions and Government R&D Institutions
- IPR policy input to Government
- Conducting training and awareness programme on IPR in the country
Technology Development and Transfer in Mechanical Engineering & Industry:
The main aim of the Department of Science and Technology is to promote the use of technology in different fields, as they have been promoting projects which are inclusive of materials, processes and devices. The Programme under the DST has been solely focused on developing technologies whether it may be in the emerging sectors or the traditional sectors, as feasibility of new ideas is always needed so that there can be a new potential invention to get a product into the market.[8]
Issues related to Mechanical Engineering related inventions:
The patent regime is the Hail Mary of protection that is available with an invention under law as it provides the description that helps identify and understand the invention with a textual description.
At the end of the tunnel, there are embodied inventions that are there to serve a specific purpose and fulfill the need of the industry as both embodied and described inventions perform a vital role in the growth of the regime of Patent. It is pertinent to mention that the statistics referred above portray the true picture of our industry which shows that the ratio of India resident to file for a patent application in comparison to foreign residents at the Indian Patent office is laughable even though there has been growth spurt in the number of patent applications filed under mechanical industry in the previous decade.
Gearing, wind motors, supplying combustible mixtures to combustion engine, cyclically operating valves, spring and shock-absorbers are the main area of focus when the functioning of the foreign companies is taken into consideration and similarly Indian Companies are attempting to aim their focus on the said sectors as well but the only drawback in the case of Indian companies is that they are less focused on fluid-pressure actuators, controlling of combustion engines and refrigeration. It is the arrival of the Make in India plan that has lead to the growth and promotion of the automobile sector and the power transmission and distribution.
Case Laws related to Mechanical Engineering Patents in India:
Several times patents get rejected under certain circumstances when invention comes under the purview of Section 3 of Indian Patents Act, 1970. Section 3[9] of The Indian Patents Act, 1970 describes the non-patentable inventions. Some of the Patents which got rejected are:
1. A patent called Gravity wheel having a perpetual motion machine got rejected. As, the invention claims to produce a powder distribution wheel which is a gravity-driven perpetual motion machine. This machine claimed to never stop except human means. Affirmation is a fixed engine of unlimited size, capable of generating continuous energy from gravity. The patent has been abandoned under Section 21 (1) on the basis of Section 3 (a) because of its performance contrary to the law of thermodynamics.Sec 3(a) states that an invention which is frivolous or which claims anything obviously contrary to well established natural laws is not registrable under Patent Law in India.
- An application for a patent, called “Electro-Mechanical Sexual Stimulation Device”, [10] was denied under Section 3(b) of the Patents Act, stating that an invention uses its primary or intended purpose or commercial exploitation of which may be contrary to public order or morals or cause serious prejudice to the life or health of humans, animals or plants or the environment.
This patent relates to sexual stimulating vibrator and its commercial use or exploitation is contrary to public or ethical order and therefore the patent has been denied based on Section 3 (b).
[1] https://www.ibef.org/industry/engineering-india.aspx
[2] https://www.omicsonline.org/mechanical-engineering-innovations.php#:~:text=Mechanical%20Engineering%2Dinnovations,%2C%20spacecraft%20and%20machine%20tools).
[3] http://nopr.niscair.res.in/bitstream/123456789/33194/1/JIPR%2020(5)%20305-319.pdf
[4] https://www.wipo.int/edocs/pubdocs/en/wipo_pub_941_2019.pdf
[7] https://dst.gov.in/technology-development
[8] https://dst.gov.in/technology-development-and-transfer
For more information on Patent Rights, Mechanical Engineering & industry in India please contact us at info@ssrana.com or submit a query.
Read More








